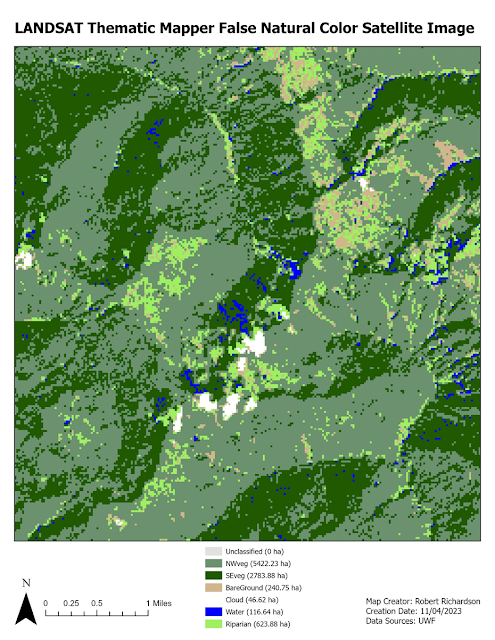
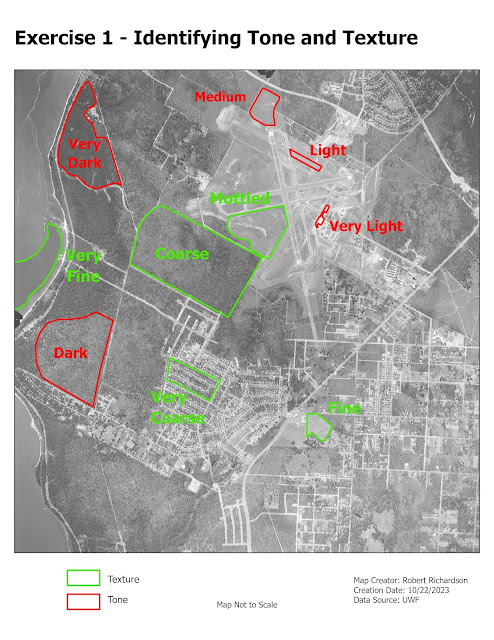
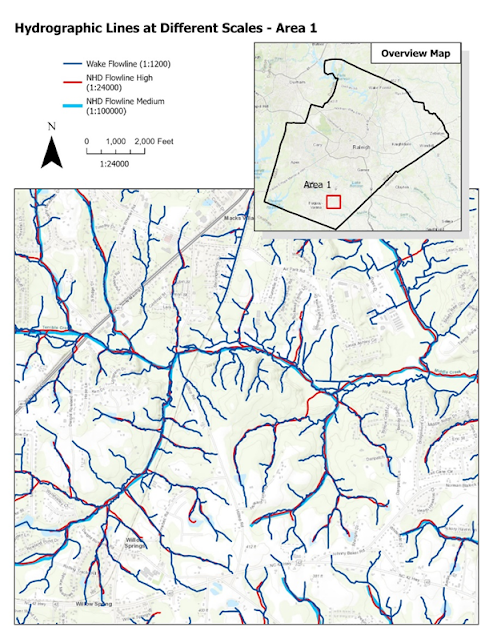
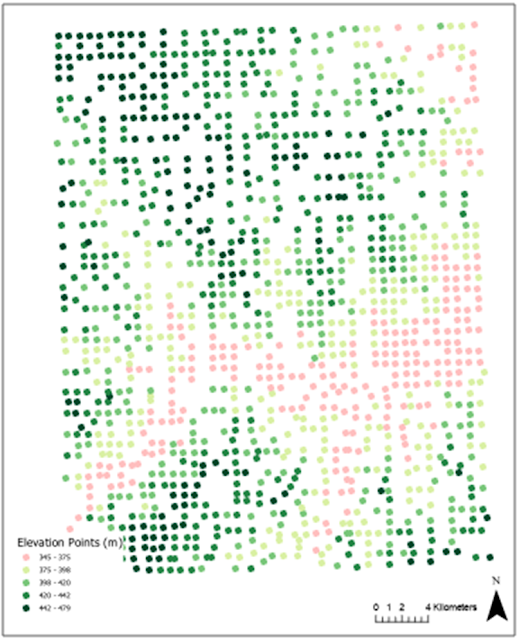
Visual interpretation is a way of extracting features from an aerial photograph. One technique involves using visual characteristics of an image. These characteristics include size, shape, tone, texture, pattern, and shadow. The first part of the lab involved the use of tone and texture to extract features. The tone element refers to the brightness or color of an object based on the amount of light reflected from an object. Objects that are darker have less light reflected. Objects that are lighter reflect more light. The texture element determines the visual smoothness or coarseness of the image. The variations of tone and texture elements help to bring out different features in the landscape. The map below shows the use of tone and texture to interpret features from an 8-bit aerial image. The next part of the lab was to identify features from an 8-bit black and white image using four different criteria. The four criteria were shape and size, shadow, pattern, and association. The